Home > International Cooperation > Fiscal Year 2000 > Energy Efficiency Workshop in 2000 > Workshop Agenda 2000
Main content starts here.
Update:April 1, 2010
Workshop Agenda 2000
CTI ENERGY EFFICIENCY WORKSHOP 2000
1. BACKGROUND

ICETT Overview
The International Center for Environmental Technology Transfer (ICETT), implements, under the guidance of the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI) in cooperation with the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), human resource development and capacity-building support to developing countries through its various training, workshop and research projects. Since 1992, the Center has received 2,357 professional participants from some 52 countries. The training, workshop and research projects focuss on two major areas; environmentally friendly conservation and sustainable development. The training, workshop and research projects are between several days and three months. ICETT will deliver the expected outcomes through substantial case-studies and discussion, and field study visits to provide insights into Japan's development experiences. It consists of two modules: (1) energy saving and (2) cleaner production.
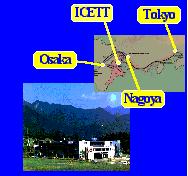
ICETT Location
The Capacity Building Working Group of the Climate Technology Initiative (CTI), which is comprised of OECD member countries and the European Commission, convened in a series of Energy Efficiency Workshops, October 5-10, 1998 and September 18-26, 1999, at the International Center for Environmental Technology Transfer (ICETT), Mie Prefecture, Japan. With the cooperation of the Japan New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), ICETT implemented and hosted the workshop at their workshop facility in Yokkaichi City, Mie Prefecture.
Following the Energy Efficiency Workshop in FY1999, ICETT will hold the CTI Energy Efficiency Workshop, from September 10 to 23, 2000, targeted for fifteen (15) participants from five countries with developing economies, the People's Republic of China, Indonesia, the Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam. The mission of the CTI is "to promote the objectives of the U.N. Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) by fostering international cooperation for accelerated development and diffusion of climate-friendly technologies and practices including greenhouse gases."
2. OBJECTIVES
The objectives of this CTI workshop will be:
- (1) to transfer information about energy efficiency technologies to and among developing countries;
- (2) to identify and overcome barriers to implementation of climate-friendly technology;
- (3) to identify future directions and activities for energy-efficient technology transfer;
- (4) to receive participant feedback in order to improve the content and effectiveness of future workshops; and
- (5) to share workshop conclusions with delegates to the UNFCCC Sixth Conference of Parties (COP6), the Netherlands.
3. WORKSHOP CONTENTS
1. Title:
CTI Energy Efficiency Workshop
2. Duration:
From September 10 to 23, 2000
3. Number of Participants:
15 participants from China, Indonesia, the Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam. (three persons from each country)
4. Workshop Justification:
Developed countries and developing countries recognize that energy saving and environmental conservation with regard to issues of climate change are global issues and that we need international cooperation in order to deal with these problems. In Asian developing countries, there has been a rapid expansion of industrialization. There is also a growing recognition that energy- efficient technologies and approaches, and policies on energy saving are urgent issues to be solved in order to maintain sustainable development.
5. Workshop Activities:
Workshop activities will include lectures, interactive discussions, country study reports, and industrial site visits in the Chubu Region. The lectures and discussions will be focused on energy- efficient technologies, approaches, and policies that are being developed and implemented in the United States, Australia and Japan. Specifically, the workshop sessions will highlight such topics as existing and emerging energy-efficient technologies, cleaner production, the beneficial reuse and recycling of materials, the importance of low cost good maintenance practices and human resources development, existing information sources, and national energy efficiency program elements and strategies. In addition, the participants will share their own expertise and present reports on their nations' energy use and activities for energy efficiency.
A wide range of energy- efficient technologies and practices will be explained and discussed. Technology transfer barriers, such as accessing information, evaluating the reliability of information and technologies, overcoming the disincentives of existing energy pricing structures, and the practice of transferring older, more inefficient technologies to developing nations, will be discussed. Participants and lecturers will work together to identify steps that could help overcome these barriers.

Training Overviiew
Participants:
Participants will learn about global climate issues, energy saving, resource saving and cleaner production, and will acquire knowledge about energy-efficient technologies and cleaner production, including sector-specific technologies and renewable energy.
The participants will acquire the skills necessary to plan, manage and implement energy-efficient activities, technologies and cleaner production in their facilities to support their countries' environmental and energy efficiency objectives.
Moreover, the participants will be managers who work with energy saving and / or cleaner production in industries in Asian countries. They will attend this workshop primarily to learn how and why to pursue activities for energy efficiency and for cleaner production in their companies. Some may also have leadership roles in their country and are expected to help influence national policy. They will be interested in and want to learn about broader global environmental issues and government activities, however, their primary role is managing facilities, particularly for energy saving and cleaner production. As such, they are the only people who can implement the actual technological and procedural changes that will reduce the gases caused by industrial energy use which are responsible for global warming. They will expect to leave this workshop prepared to identify and implement energy efficiency programs in their companies.
Participants are engaged in government organizations, administrative agencies, manufacturing industries and energy production related organizations, as follows:
Participants are to:
- (1) be engaged in the following fields:
- - energy saving, and / or cleaner production work in an enterprise;
- - preferably of manager status in government organizations, administrative agencies, manufacturing industries and energy production related organizations.
- (2) be a university graduate of science or posses equivalent knowledge and/or professional experience;
- (3) be in good health so as to undertake the workshop program;
- - Due to health concerns, pregnant women may not participate in the program.
- (4) have a fluent command of English;
- (5) have systematic understanding of industry processes and decision making;
- (6) currently have a leadership position;
- (7) know how to find, access, and use information sources, experts, and tools;
- (8) have an enthusiastic attitude towards improving the problems of global warming through energy efficiency and cleaner production;
Resource Persons:
The core group of resource persons from the USA, Australia and Japan will bring a variety of expertise and experiences to the workshop which will last for a week. They should remain focused on the needs of the workshop participants, which are to acquire knowledge, motivation, resources, and the know how for planning and practical implementation. Given this, the resource persons should have experience working directly with industry and with industrial energy-efficient technologies and cleaner production. They should be familiar with the obstacles plant managers face in implementing these technologies and notions, and with the approaches that engineer experts can use to overcome these obstacles. They should plan to work directly with participants on problem-solving exercises for specific plant issues. The resource person's role is to assist the workshop participants and to help create a positive situation for effective learning and communication. Particularly, the resource person will help ensure that the workshop has defined the correct objectives and that the workshop then remains focused on achieving those objectives. The resource person is also responsible for implementing, with input from participants, the discussion sessions and for facilitating these discussion sessions. The resource person will also help moderate the sessions and keep track of time and the agenda. The sessions will last for a week.
Organizers:
ICETT is responsible for the overall execution of the Workshop. They will provide the facilities, arrange the agenda and field trips, manage the budget, advertise the workshop to find participants and lecturers, manage the follow-up to COP6, and ensure that all administrative aspects of the Workshop fit together and function smoothly. They will provide rooms for resource persons, materials for exercises, and computers for internet training.
In addition, they will prepare a message for COP6, summarizing the workshop results and recommendations, in cooperation with resource persons, and they will recommend ways to improve future CTI workshops.
4. PROGRAMME
In order to achieve the above-mentioned objectives and motivate the participants, ICETT will provide lectures, tutorials, plant-visits and discussion with resource persons from Australia, the USA and Japan. In particular, methodological case-studies and practical workshops will be highlighted.
In addition to regular training session programmes, special programmes will be introduced, such as workshop sessions held on September 14-16 and September 21-22. The participants will examine how to promote energy saving measures, energy efficiency and cleaner production, and create a technical brochure and workshop report, as output from the sessions.
Session 1-1 Orientation Programme
In this session, participants will be provided with the general information that will help them have a comfortable stay at ICETT. Expectations from the workshop will be elicited from the participants to find common ground between needs and wishes on these sessions.
Objectives:
The participants will:
- (1) be introduced to the workshop programme, and clarified their own expectations and roles.
- (2) be familiarised with daily life in Japan.
Discussion Topics:
- What are your expectations from this workshop?
- What are the priority problems and issues in your current work?
Session 1-2 Keynote Lecture
The keynote lecture will be provided by the Global Environmental Technology, Japan's Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI), describing an introduction to the Climate Technology Initiatives (CTI). This session will highlight the CTI's objectives and roles, fostering international co-operation for accelerated development and diffusion of climate-friendly technologies and practices relating to greenhouse gases. In particular, CTI activities aim to: (1) collaborate closely with developing countries and economies in transition; (2) work in partnership with stakeholders, including the private sector, non-government organizations (NGOs), and other international organizations; and (3) motivate effective energy saving technology.
Objectives:
The participants will:
- (1) be introduced to CTI activities, with a focus on research programmes
- (2) be given an explanation of CTI in relation to UNFCCC
Session 2 Government Energy Policies and Programmes
In this session, we will focus on the energy saving policies of two governments, such as those of the USA and Japan. This will introduce the effectiveness of harmony between a healthy environment and sustainable development, giving examples of US and Japanese energy policies and management from the perspectives of energy professionals.
In the Japan's session, the lecture will examine the Japan's energy conservation activities, such as Japan's Energy Policy, Electricity Demand Management as the Japan's energy trends, Effective Activities of Education and Measurements and so on. In particular, the lecture will be given an example of Energy Conservation Center of Japan.
Objectives:
The participants will:
- (1) examine energy efficiency and power technologies for the improvement of economic and environmental performance
- (2) be introduced to Japan's energy saving policies
- (3) understand CTI in relation to UNFCCC
Discussion Topics:
What have you seen and heard in this session?
Session 3-1 Country Presentation
In this session, this module will preface the workshop. The successes and problem factors of industrial policies will be explained by the participants.
Objectives
The participants will come to recognize the similarities and differences between issues in different countries.
Discussion Topics:
What have you seen and heard in this session?
Session 3-2 (4-2, 9-2, 10-1) Plant-visits
In this session, case-studies undertaken by the Chubu Electric Co. Ltd., the Hisai-Sakakibara Wind Farm, the Taiheiyo Cement Co. Ltd., and Imuraya Co. Ltd. will be dealt with. The studies are about company-based or industrial-based environmental management such as energy saving, recycling, energy efficiency and cleaner production. This session will include two plant-visits: to the Chubu Electric Co. Ltd. and to the Hisai-Sakakibara Wind Farm, highlighting case-studies of energy savings and new energy technology in the first module of "Energy Savings". In the second module of "Cleaner Production", participants will be encouraged to make comparisons with Australian and Japanese case-studies of cleaner production. The plant-visits will be to the Taiheiyo Cement Co. Ltd. and to Imuraya Co. Ltd.

![]()


Objectives:
The participants will grasp the mechanism and flow-chart process of energy saving and cleaner production mechanisms, as follows:
Chubu Electric Co Ltd: the theme is resource saving and energy saving
Hisai-Sakakibara,: the theme is Japanese wind farms
Taiheiyo Cement Co Ltd: the theme is recycling and cleaner production
Imuraya Co Ltd: the theme is compost and cleaner production
Discussion Topics:
What have you seen and heard during the plant-visits and informal talks that you feel is worth learning more about to enable you to carry out your work more effectively?
Special Session Programme 4-1 Energy- Efficient Technology (1)
Is the Japanese promise to reduce CO2 6% at the basis of 1990 by the year of 2010 possible ?
Discussion Topics:
- (1) How energy is consumed in Japan; from the view of Life Cycle Assessment.
- (2) Advanced technologies now available to reduce CO2 emissions.
- (3) Challenge to realize the promise; top runner method, possible industrial contributions.
- (4) A simple method to simulate future energy consumption in Japan: Energy consumption per capita x population.
- (5) A simple but possible energy consumption estimation.
Special Session Programme 5-1 Energy-Efficient Technology (2)
Discussion Topics:
What is the status of Energy Efficient Technology in your country?
- (1) How is energy consumed ?
- (2) Which kinds of energy-efficient technologies are or will be available ?
- (3) How would you apply this simple but possible energy consumption estimation to your country?
Session 5-2 Energy Savings Technology
In this session, we have two technical sessions on energy savings and cleaner production technologies.
The practical know-how and the case-studies of energy savings in the Japan's plants will be explained.
As we faced the oil crisis in 1973, we have promoted the energy savings in the industrial sectors. In Japan, we have had management targets and considerable operation of the energy savings on manufacturing process in the plants. This session will give examples of "electric energy" and "heat energy".
Special Session Programme 6-1 Energy Efficient Technology (3)
Discussion Topics:
- (1) How are you able to realize the scenario above ?
- (2) The most important aspect is to promote incentives. What are possible incentives in your country?
- (3) Find win/win opportunities in international relations.
Special Session Programme 8-1 Cleaner Production Programme (1)
Introduction to Cleaner Production
This lecture seminar explores the birth of the concept of Cleaner Production and details the importance of Cleaner Production in the sustainability agenda. We examine the need for a business approach which incorporates the strategy and discuss the benefits which may be obtained.
The following important points are made:
- (1) The importance of globalisation and the links with sustainable development
- (2) How business views sustainable development
- (3) Profiting from a sustainable approach
- (4) How Cleaner Production was born and what it means
- (5) How business benefit from a strategic approach
- (6) The UNEP network
Session 8-2 Cleaner Production technology
In this session, we will highlight the cleaner production technology (CPT), following the definition of UNEP-TIE and comparing to the end-of-pipe technology (EOP). This covers the CPT's scopes, economical aspects, advantages and CPT's application for the developing countries, giving some examples of Japan's case studies. In particular, we will learn the substantial case of cleaner production technology on manufacturing process of the chemical plants in People's Republic of China. The lecturer will give us the significant remarks of the installation of cleaner production.
Special Session Programme 9-1 (10-2) Cleaner Production Programme (2)
Cleaner Production - Programme and Technology
These lectures explore the implementation of Cleaner Production in a company. The lectures deal with all the basic system problems inherent in developing a Cleaner Production approach and finally successfully instituting a programme. Many case studies are presented during the talks, showing how various activities have been successful for different companies.
The following points are covered:
- (1) A lifecycle approach to management
- (2) The importance of change and its management
- (3) Developing a programme
- (4) Management commitment
- (5) Planning a programme
- (6) Preliminary stages - data collection and verification, consultation and initial assessments
- (7) Developments of options
- (8) Feasibility analysis
- (9) Implementation, monitoring, review and feedback
The lectures are delivered in an interactive mode with the students participating from their level of experience. Videos may accompany the lectures to highlight points made. These two lecture workshops will provide particpants with a good overview of how Cleaner Production programmes are put together and how to carry out an assessment on a site.
Session 11 (12-1) Brochure and Workshop Report
Objectives:
The participants will be required to deal with various problems and issues after gaining some new knowledge and skills. The participants will grasp the problems and issues that need to be dealt with and solved in their current work.
Discussion Topics:
- Which priority problems or issues can be solved within six months to one year?
- Which problems require long-term solution?
- Can you deal with them alone with the cooperation of the office you belong to?
- What will enable you to deal with these priority problems and issues?
- What information is necessary?
- What skills will help you deal with the present situation?
5. WORKSHOP INSTITUTIONS :
All documents from participants should be submitted to:
Ms Noriko SUGIMOTO
c/o Inter Group Corporation
Sakae East Bldg., 4-2-7 Sakae Naka-ku Nagoya, 460-0008 JAPAN
Phone: 81-52-263-6334 FAX: 81-52-263-6298
E-mail: convention-ngo@intergroup.co.jp
(Person-in-charge, Mr Hide MASHITA, Survey and R&D Division)
International Center for Environmental Technology Transfer (ICETT)
Address: 3690-1, Sakura-cho, Yokkaichi, Mie 512-1211, Japan
Phone: 81-593-29-3500 Fax: 81-593-29-8115
URL http://www.icett.or.jp