Home > Research and Analysis > Research > Fiscal Year 2015 > JICA Technical Cooperation Project Completed for NOx Total Emission Control in China
Main content starts here.
Update:October 18, 2016
JICA Technical Cooperation Project Completed for NOx Total Emission Control in China
Background
In China, NOx emissions have been increasing because of rapid economic growth and a growing number of automobiles. In the twelfth five-year plan (2011 to 2015), for this reason, China designated NOx reduction as one of the key indicators illustrating its goal to reduce the total emissions of main pollutants. The thirteenth five-year plan, which has just started in 2016, also continues to maintain compulsory NOx reduction goals. As a joint venture, ICETT formed an expert team together with Suuri-Keikaku Co., Ltd. and, from March 2013 to March 2016, implemented a capacity building program to provide related personnel with assistance in technology, policies, and systems to reduce total NOx emissions.
Outline
The project aims at improving NOx emission control measures in China. It has two main goals: 1) the formulation and use of technical guidelines for NOx emission control, and 2) the improvement of measures to understand the effect of NOx control with the use of air pollutant diffusion simulation. ICETT took charge of the activities to achieve the first goal as stated below.
ⅰ) Examining the amount of NOx emissions and proposing improvement methods for model companies
Target companies in Xiangtan, Hunan Province, were selected from the cement, steel sintering, and industrial boiler fields, which were covered by the technical guidelines. Then, emissions of air pollutants, such as NOx, were examined and measures to reduce them were offered in accordance with the emission conditions in each company. The selected businesses began gradually with measures that required less renovation and only limited financial investment, but have already shown a certain degree of success.
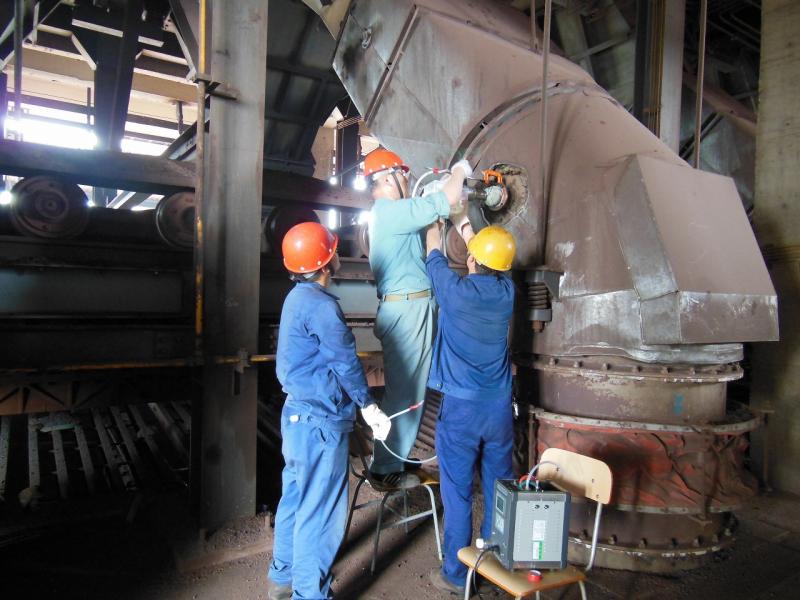



ⅱ)Training course in Japan
An eleven-day course was held in Japan for government officials engaged in air pollution control affairs in China. The Chinese participants learned about the Japanese legal systems concerning NOx control, the roles of local administration, and reduction efforts by companies as emission sources. This way, they had an opportunity to examine various measurs to control NOx emissions, which can also be introduced to China.
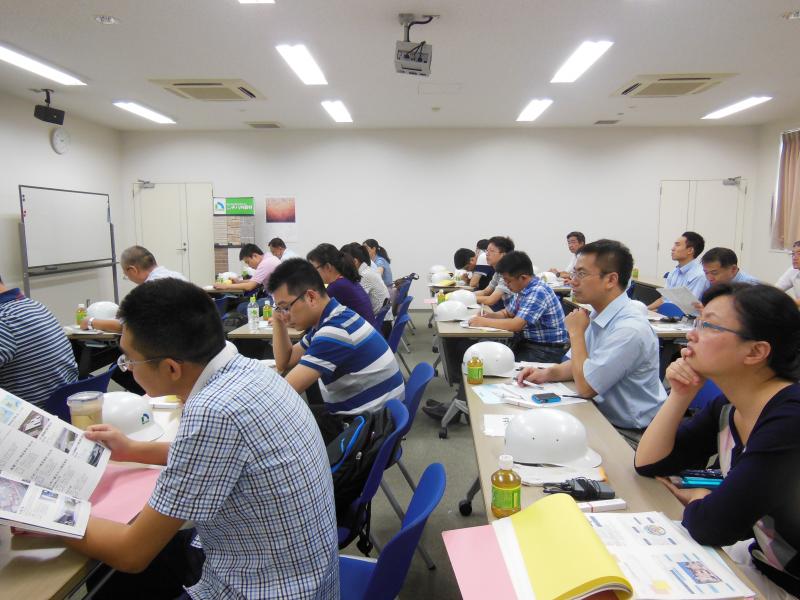
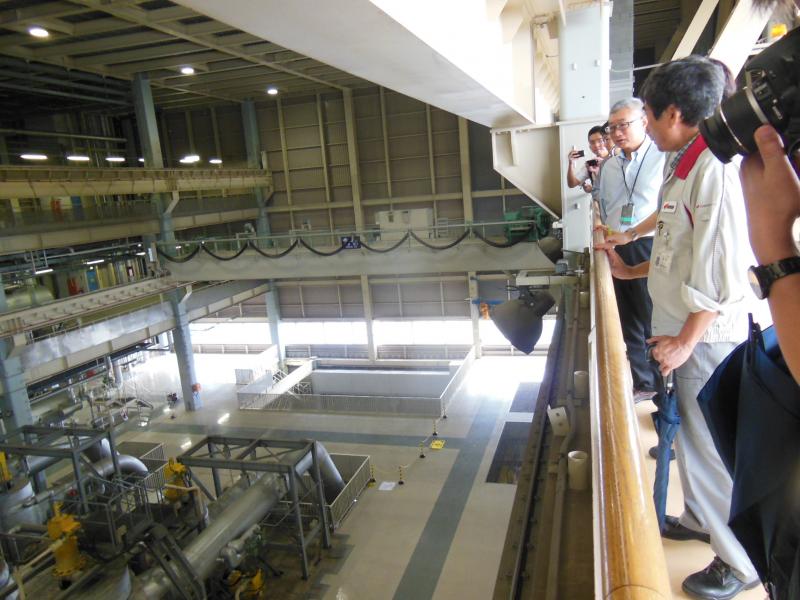


ⅲ)Seminars and other events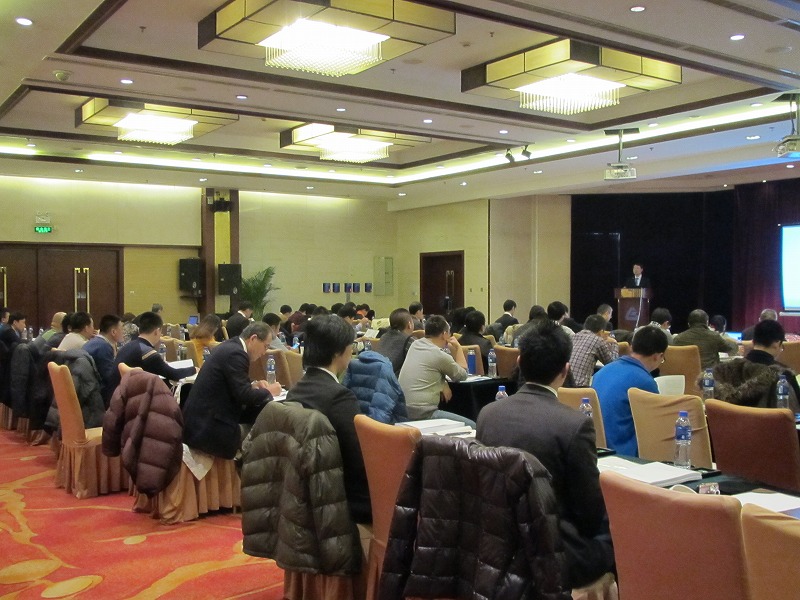
During the three-year period of this project, seminars and technical exchange events took place for Chinese government officials, staff members from companies of industries that especially require NOx control, and those from businesses which manufacture equipment for environmental protection. The exchange events were also attended by Japanese companies which own useful technology for NOx control. There were lively exchanges of opinions about the current NOx situation in China and the Japanese NOx control technology which can also be used in China.
ⅳ)Formulation of technical guidelines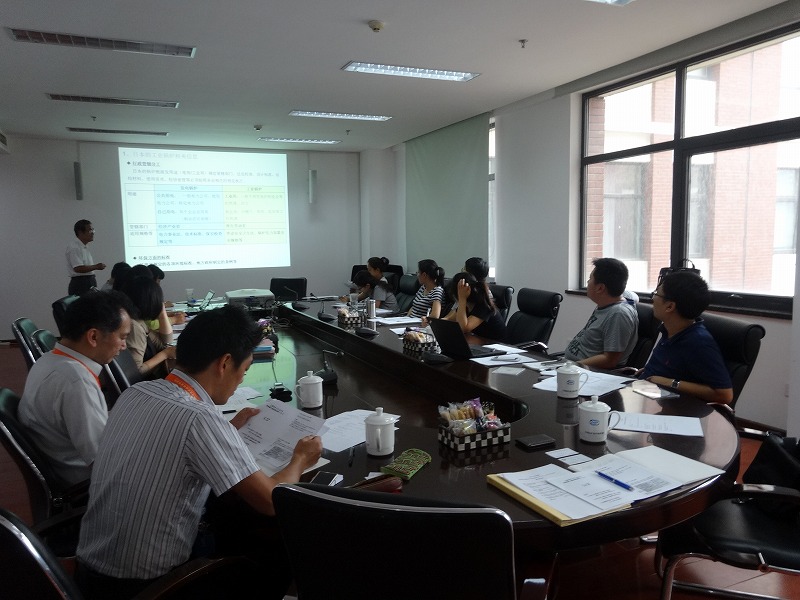
Based on the above-mentioned activities, technical guidelines were drawn up for NOx control technology suitable for the situation in China. The guidelines featured four fields in which China puts importance on NOx control: cement production, coal-fired power generation, industrial boilers, and steel sintering and coke ovens. Meetings with Chinese experts from these fields were carried out to draw up and examine the technical guidelines so that they would be adopted more easily and smoothly. At a workshop to promote them in China, the completed guidelines were distributed to those responsible for environmental management at companies and local governments.
The project ended in March 2016, but the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China is highly expected to play a major role in the future in encouraging the introduction of NOx control technology that best suits China’s changing conditions, while it continues to update the technical guidelines based on newly established regulations and rules.